Advertisement.
EnchantedLearning.com is a user-supported site.
As a bonus, site members have access to a banner-ad-free version of the site, with print-friendly pages.
Click here to learn more.
(Already a member? Click here.)
Old Questions
Questions from May 1999
Q: What were the predators of the ultrasouros?
from Christian B., rochester, mi, USA; May 31, 1999
A: There is no fossil evidence that points to particular predators of Ultrasauros. All you can do without real evidence is guess, based on which large meat eaters lived during the same time and place. For a list of its contemporaries in the USA during the late Jurassic period, click here and look for very large theropods (in the yellow section about North America). For more info on Ultrasauros, click here.
Q: Where did Pterodactyls Live
from nton A., Sunnyvale, CA, USA; May 31, 1999
A: There were many different species of Pterodactyloids, including Pterodactlyus (which lived in what is now Tanzania, England, France, and Germany), Quetzalcoatlus, Dsungaripterus, Pteranodon, and others.
Q: My three year old daughter would like to know how T-Rex cleaned his teeth. We've asked the question twice on zoom,dinosaurs and haven't seen it posted yet. Why? She's really looking forward to seeing her name and finding out an answer to her question. Please respond ASAP.
from Grace M, hicksville, NY, USA; May 29, 1999
A: Why, because I have over 300 questions in my mailbox that are unanswered and I only have time to answer a few a day.
 No one knows how a T. rex would clean its teeth or if it even needed to. Since it had replaceable teeth, it probably didn't need to clean its teeth. If one broke off or became worn down, it would be replaced by a new tooth. For more information on T. rex, click here.
No one knows how a T. rex would clean its teeth or if it even needed to. Since it had replaceable teeth, it probably didn't need to clean its teeth. If one broke off or became worn down, it would be replaced by a new tooth. For more information on T. rex, click here.
To answer questions about behaviors like this, paleontologists usually look at modern-day animals that have some similarities. To hypothesize about T. rex's teeth, look at living meat-eaters with replaceable teeth (like sharks, who don't clean their teeth).
This is not an answer I would have liked to have told my children when they were three, since getting them to brush their teeth was (and still is) very difficult. You might want to add that dinosaurs didn't eat sugary things, so tooth decay was not a problem for them.
Q: What is the original species that evolved into the dinosaurs?
from Loren J., Harbor Beach, Michigan, USA; May 28, 1999
A: Thecodonts (not a species) were the animals that evolved into the dinosaurs during the Triassic period. These socket-toothed reptiles were the ancestors of dinosaurs, birds, pterosaurs, and crocodilians. The exact thecodont that gave rise to the dinosaurs is unknown.
Q: How did dinosaurs ensure that a species would continue?
from Darryl B., Harbor Beach, Michigan, USA; May 28, 1999
A: The same thing that other species do, live long enough to produce offspring.
Q: Was there any dinosaur that had nostrils on the top of its head besides Diplodocus?
from Jared and Mary, West Seneca, New York, USA; May 28, 1999
A: All the diplodocid dinosaurs, the camarasaurids, and the brachiosaurids had nostrils over their eyes.
The diplodocids include: Apatosaurus, Amphicoelias, Barosaurus, Cetiosauriscus, Dicraeosaurus, Diplodocus, Microdontosaurus, Mongolosaurus, Nemegtosaurus, Quaesitosaurus, Seosmosaurus, Supersaurus, and Torneria.
The camarasaurids include: Algoasaurus, Aragosaurus, Asiatosaurus, Camarasaurus, Cathetosaurus, Chiayuesaurus, Opistocoelicaudia, and Parrosaurus.
The brachiosaurids include: Astrodon, Bothriospondylus, Brachiosaurus, Damalasaurus, Dinodocus, Dystylosaurus, Giraffatitan, Lancangjianosaurus, Pelorosaurus, Pleurocoelus, Rebbachisaurus, and Ultrasauros.
Q: Fossils found in Utah?
from Sarah G., south jodan, Utah, USA; May 28, 1999
A: For fossils found in Utah (and other US states ad Canadian Provinces), click here.
Q: Stegosaurus and Stegoceras are easy to mix up by someone who doesn't spell dinosaur names correctly. Are there any other dinosaurs like this??
from Jimmy L., Georgia, USA; May 28, 1999
A: Megalosaurus and Megaraptor, Majungatholus and Majungasaurus, Asiaceratops and Asiatosaurus, Archaeornithoides and Archaeornithomimus, Dryptosauroides and Dryptosaurus, Cetiosaurus and Cetiosauriscus, Struthiomimus and Struthiosaurus, Valdoraptor and Valdosaurus, Zigongosaurus and Zizhongosaurus, and many, many others. Beware spelling errors and typos!
Q: How much do a Trachodon weigh?
from Arielle L., Cinnaminson, NJ, USA; May 28, 1999
A: Trachodon is only known from a few teeth. it's impossible to deduce its weight from so little information. For more information on Trachodon, click here.
Q: Why are similar dinosaurs found on different continents?
from Daryl E., Harbor Beach, Michigan, USA; May 27, 1999
A: During the Mesozoic Era, when the dinsoaurs lived, the continents looked different than they do today. Towards the beginning of the Mesozoic, the continents were jammed together into a supercontinent called Pangaea. Dinosaurs (and other animals) could move from continent to continent on land. Later during the Mesozoic Era, the continents started to drift apart.
Q: were can I find a stegasoras site
from Hugo, ?; May 27, 1999
A: Click here for Stegosaurus. If you want Stegoceras (a thick-headed dino), click here.
Q: Are birds and dinosaurs related?
from Amanda B., Quantico, VA; May 26, 1999
A: Yes, the birds most likely evolved from dromaeosaurid dinosaurs. For more information, click here.
Q: Which of these are dinosaurs: Pteranodon, Coelophysis, Saber toothed tiger, Peloneustes, dinichthys, Parasaurolophus, and Protoceratops?
from Jena B., Vallejo, CA, USA; May 27, 1999
A: Coelophysis, Parasaurolophus, and Protoceratops. To see what the other creatures were, look for them in the Dino and Paleontology Dictionary.
Q: where can you find about their babies for a report
from Chelsea B., Spring Green, WI, USA; May 26, 1999
A: Click here for some information on hatchlings, eggs, etc.
Q: How long were the claws of the velociraptor?
from Geoffrey B, St. Laurent, Quebec, Canada; May 24, 1999
 A:
A:
Velociraptors had a 3.5 inch (9 cm) long, sickle-like, retractible claw was on the middle toes of each foot. This claw was its main weapon, and could probably kill most of its prey (defenseless plant-eaters like hadrosaurs) easily.
For more information on Velociraptor, click here.
Q: do dinosaurs have feelings?
from kaleem, Toronto, Ontario, Canada; May 24, 1999
A:
No. Complex emotions would require a much larger brain than dinosaurs had.
Q: how tall is t rex
from Michael R., Frankfort, NY, USA; May 23, 1999
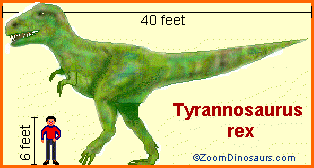 A: Tyrannosaurus rex was up to 40 feet (12.4 m) long, about 15 to 20 feet (4.6 to 6 m) tall, and roughly 5 to 7 tons in weight. For more information on T. rex, click here.
A: Tyrannosaurus rex was up to 40 feet (12.4 m) long, about 15 to 20 feet (4.6 to 6 m) tall, and roughly 5 to 7 tons in weight. For more information on T. rex, click here.
Q: Do you have any information on Noasaurids?
from Mary H., Tacoma, WA, USA; May 23, 1999
A: I've never heard of Noasaurids, but Nodosaurids were a type of ankylosaur. For more information on these armored dinosaurs and other ankylosaurs, click here.
Q: What were some of the plants when the dinosaurs lived and what was the environment like?
from Allison O., Broomall, Pennsylvania, USA; May 23, 1999
A: See the page on the Mesozoic Era.
Q: What is the common name and scientific name of a Nanotyrannus dinosaur?
from John K., Winfield, IL, USA; May 22, 1999
A: All of the dinosaurs are known commonly by their scientific name. Nanotyrannus is both a scientific genus and that dinosaur's common name. For more information on Nanotyrannus, click here.
Q: i would like any and all information available on the plateosaurid family of dinosaurs, including(if possible), maps and charts as well as text, for a science project
from leif g, tacoma, Washington, USA; May 21, 1999
A: For an entry on Plateosaurids in the Dinosaur Dictionary, click here. Also, see the pages on Plateosaurus and Massospondylus, and look up the other plateosaurids in the Dinosaur dictionary. For maps and infor about the late Triassic and Early Juassic periods (when Plateosaurids lived), click here.
Q: which countries were dinosaurs found in?
from ?; May 21, 1999
A: See this section of Zoom Dinosaurs for a list of where dinosaurs have been found (by continent, country, state/Province).
Q: When was the last dinosaur found and where?
from John; May 21, 1999
A: Dinosaurs are being found all the time, all over the world. Paleontologists usually take some time to examine the fossils before reporting the find. A large find was announced about a month ago; James I. Kirkland (of the College of Eastern Utah's Prehistoric Museum) discovered about 10,000 fossilized Ankylosaurid and Nodosaurid bones near Price, Utah. For dinosaur news items and recent finds, click here.
Q: Could the dinosaurs survive cold. (winter)?
from Rahun; May 21, 1999
A: Most dinosaurs lived in warm environments, but some did live in cooler environments (like the extremes of northern and southern Pangaea). Paleontologists think that some of these cool-area dinosaurs (like Edmontosuaurs) may have migrated to avoid the worst part of the winter. Some dinosaurs may have used other survival strategies, like hibernation.
Q: What where the dinosaurs that walked California?
from Debbie G., BullheadCity, AZ, USA; May 20, 1999
A: For dinosaurs found by state (or Province) and country, click here.
Q: Is there such thing as a raptor like the one on the movie
Jurasic Park? If so did they look the same as the movie raptor and acted the same?
from Amanda M., New Haven, West Virgina, USA; May 18, 1999
A: The velociraptor in Jurassic park was almost twice as big as the real thing. Also, it was WAY too intelligent in the movie. For factual information on Velociraptor, click here.
Q: Why dosen,t the Protocerotops have any horns on its head and has a slanded sheeld
from Josh G., West Seneca, New York, USA; May 18, 1999
A: No on e known why animals evolved particular characteristics, except that these features worked in their environoment. It's like asking why we have five fingers and not six or four (or some other number).
Q: What time period did the Tyrannosaurs Rex.
from John K., Seneca, New York, USA; May 18, 1999
A: T. rex lived during the late Cretaceous period (at the end of the Mesozoic Era. For more information on T. rex, click here.
Q: What can you tell me about the Allosaurus?
from Brittany B., APO, AE, Iceland, USA; May 18, 1999
A: For an information sheet on Allosaurus, click here.
Q: What type of plant flourished during the dino era?
from carol m., chula vista, california, USA; May 18, 1999
A: Conifers, fern, club mosses, horsetails, gingkos, cycads, and others lived during the Mesozoic Era. Flowering plants developed during the Cretaceous period, towards the end of the Mesozoic.
Q: Where did dinosaours live? What contry?
from Chris S., Spencerport, New York, USA; May 18, 1999
A: Dinosaur fossils have been found on every continent on Earth. For a list of where all the dinosaurs have been found by continent, click here.
Q: What were the predators of the Coelophysis?
from Nick O., Fairbanks, Alaska, USA; May 17, 1999
A: There is no certain fossil evidence of what Coelophysis' predators were. To see what late Triassic animals may have hunted Coelophysis, see the page on the Triassic and the page on late Triassic dinosaurs and see which meat-eaters may have been able to hunt and kill a Coelophysis.
Q: i what kind of environment did dino. live in???
from spencer o., kenner, ia, USA; May 17, 1999
A: Dinosaurs lived all over the Earth during th erelatively warm Mesozoic Era, in environments that ranged from warm and humid, to dry, forested, swampy, and cool.
Q: What is the habitat where the triceratop lives? Who are its friends and enemies. What kind of food does it eat?
from Angelo, Woodbridge, Ontario, Canada; May 17, 1999
A: Triceratops was hunted and eaten by T. rex. Dinosaurs didn't have friends like people do. Look at the information sheet on Triceratops. For information on the climate of the Cretaceous period, click here.
Q: What is the difference between endotherm and ecotherm? What is each?
from Derek S., Centerville, Iowa, USA; May 16, 1999
A: See this page.
Q: Do you have any information on the saurornitholestes dinosaur? If so where can I find it?
from Amanda W., Moorefield, WV, USA; May 16, 1999
A: I've added Saurornitholestes to the dinosaur dictionary.
Q: I am doing a research paper on the Compsognathus. What were it's enemies and how did it protect itself?
from Stephen T., San Antonio, TX, USA; May 16, 1999
A: Compsognathus protected itself with a huge sickle-like claw on each foot and many sharp teeth. Its enemies are not certain (since fossils of Compsognathus have been found with it locked in battle with another predator nor have Compsognathus bones been found in the stomach of another dinosaur). For some likely candidates, look at the list of late Jurassic dinosaurs from Europe. For more information no Compsognathus, click here.
Q: Who named Triceritops.
from Sophia D., Sun valley, Idaho, USA; May 15, 1999
A: Triceratops was named by Paleontologist Othniel Marsh in 1889. For more information on Triceratops, click here.
Q: In what era did dinosaurs go extinct
from Manuel R., national city, CA, USA; May 14, 1999
A: Dinosaurs went extinct at the end of the Mesozoic Era (about 65 million years ago).
Q: Why does Corythosaurus have that fin like thing on his head
from ManChelsea S., Plainfoeld, Indiana, USA; May 14, 1999
A: No one knows why. For information on Corythosaurus, click here.
Q: Was Ornitholestes a meat eater or vegaterian?
from Ariel K, Planfield, Indiana, USA; May 14, 1999
A: Ornithomimus was a meat-eater. For more information on Ornithomimus, click here.
Q: what are some facts about plesiosaurus? also i know they are reptiles but are they dinosaurs???
from zeina, ny, USA; May 14, 1999
A: For information on Plesiosaurus (which was not a dinosuar), click here.
Q: Where can I find info on the smilodon.
from Natan W., New York, New York, USA; May 14, 1999
A: For an information sheet on Smilodon, click here.
Q: whatdoes a wooly mamouth look like
from michael d, glendale, missouri, USA; May 13, 1999
 A: For information about the woolly mammoth, click here.
A: For information about the woolly mammoth, click here.
Q: What does it look like in Tyrannosaurus Rex's body?
from Lyndon C., Saskatoon, Sask., Canada; May 13, 1999
A: No fossilized imprints of T. rex internal structure have been found. For other information on T. rex, click here. The only dinosaur whose internal structure is at all known as of now, is the small Italian theropod Scipionyx.
Q: What was the size, weight,width, lengh and hight of the Denversaurus
from Tara G., Maffra, Victoria, Australia; May 13, 1999
A: Denversaurus is a doubtful genus; it is likely the same dinosaur as Edmontonia; for information on Edmontonia, click here.
Q: Yes, I was wondering if there was more theories of extinction for dinosaurs.
from Joseph L., Waipahu, Hawaii, USA; May 13, 1999
A: Yes, click here.
Q: what kind of dinosuars lived in pennsylvania?
from Maureen D., Omaha, NE, USA; May 14, 1999
A: For dinosaurs found in Pennsylvania (and other parts of North America), click here.
Q: How do you know a dinosaurs speed?
from Adrian G, Tinamba, Victoria, Australia; May 12, 1999
A: For information on dinosaur locomotion, click here.
Q: do dinosaurs turn into oil when they die
from joe, washington, new jersey, USA; May 12, 1999
A: Oil found underground is the ancient remains of organic matter (plants and animals-including dinosaurs). Plastics are made from oil, so when you play with a plastic dinosaur, you may be playing with the remains of a real dinosaur.
Q: Were there any omimovore dinosaurs?
from Traci B and Joseph K., Fredrickspurg, Texas, USA; May 12, 1999
A: Yes, Oviraptor was an omnivore. For more info on Oviraptor, click here. For more info on dinosurs diets, click here.
Q: Which era has invloving insects?
from MS, Boston, Mass., USA; May 12, 1999
A: Insects evolved during the Silurian Period, over 400 million years ago. For a chart of geologic time, click here.
Q: Where was the Plateosaurus found. Where did it live? When did it Live?
from Jessica C., East London, South Africa; May 12, 1999
A: For an information sheet on Plateosaurus, click here.
Q: Please tell me about Edmontosaurus.
from Dabi M., San Antonio, TX, USA; May 12, 1999
A: For an information sheet on Edmontosaurus, click here.
Q: What does the dinasour name Gallimimus mean? What other animals lived with the dinasour Gallimimus?
from Jesie A., Dallas, Texas, USA; May 11, 1999
A: Gallimimus means "chicken mimic." To see what other other animals lived during the late Cretaceous period, see this page on the Cretaceous period and this page on dinosaurs found during the late Cretaceous in what is now Mongolia. For more information on Gallimimus, click here.
Q: what were the dinosaurs found in Africa ?
from Karis M, Mddlebury, Vermont, USA; May 11, 1999
A: Click here for African dinosaurs.
Q: where can I find dinaors' information?
from Hugo l, ?; May 11, 1999
A: Click here.
Q: What can you tell me about the Anakylsaurs?
from Nancy K., Amherst, New York, USA; May 11, 1999
A: The Ankylosaurs were heavily armored quadrupedal plant-eaters with spikes, bulky bodies, a short neck, long tail, a toothless horny beak, and leaf-shaped teeth in the cheeks. These ornithischian dinosaurs lived from the mid Jurassic period until the late Cretaceous period. Ankylosaurs are divided into the nodosaurids and the ankylosaurids. The nodosaurids (including Acanthopholis, Brachypodosaurus, Chassternbergia, Cryptodraco, Dracopelta, Edmontonia, Hoplitosaurus, Hylaeosaurus, Minmi, Panoplosaurus, Polacanthus, Sarcolestes, Sauropelta, Silvisaurs, etc.) lacked a tail club and had a narrow head. The ankylosaurids (including Ankylosaurus, Amtosaurus, Euoplocephalus, Pinacosaurus, Saichania, Sauroplites, Tarchia, etc.) had a bony tail club and a wide head. For more information, see
Q: How do dinosaurs make babies?
from Juana C., Bell Gardens, California, USA; May 11, 1999
A: They laid eggs. For more information on dinosaur reroduction, click here.
Q: were can I find information about cabondating?
from Bellafonte, PA, USA; May 11, 1999
A: Click here, but carbon dating is only useful for material under about 10,000 years old. For dating dinosaur fossils (which are millions of years old), other radioisotopes are used (like Uranium-235 or Potassium-40) to date the bracketing volcanic layers. For more information on dating fossils, click here.
Q: What do Paleontologists think is the reason for some dinosaurs living in herds?
from ??; May 11, 1999
A: Some dinosaurs live din herds for the same reasons that other animals live in herds. A herd affords some protection for its members, easily accesible mating choices, some shared care for the young, hunting groups (for carnivores), etc.
Q: Please can you name me about 10 well known dinosaurs?
from Lazarus K., Rivonia, Johannesburg, Republic of South Africa; May 11, 1999
A: T. rex, Stegosaurus, Triceratops, Apatosaurus, Styracosaurus, Brachiosaurus, Velociraptor, Compsognathus, Maiasaura, and Iguanodon.
Q: Were more dinosaurs plant eaters or meat eaters?
from Elizabeth B., Siler City, North Carolina, USA; May 11, 1999
A: Many more were plant eaters. For more information on dinosaur diets, click here.
Q: What are sintists who study fossils called ?
from jessie t., siler city, North Carolina, USA; May 11, 1999
A: They're called paleontologists. For information on some famous paleontologists, click here.
Q: What is a Pangaea
from ??; May 11, 1999
 A: Pangaea is the name of the supercontinent that existed during the end of the Permian until the Jurassic period.
A: Pangaea is the name of the supercontinent that existed during the end of the Permian until the Jurassic period.
Q: what is the dumbest dinosaur that ever lived
from lance b, san antonio, texas, USA; May 10, 1999
A: For a page on the relative intelligece of dinosaurs, click here.
Q: Where there any dinosaurus found in New York
from Corey E, Spencerport, New York, USA; May 10, 1999
A: For fossils found in New York, click here.
Q: what are five dinosaurs that were from Alberta?
from Ryan and Mike, AB, Canada; May 10, 1999
A: For Canadian fossils by province, click here.
Q: Do you have any information about the dinosaur Iguanodon?
from Amelia B., Woodbury, NJ, USA; May 9, 1999
A: Yes, for information on Iguanodon, click here.
Q: WELL I ACTUALLY HAVE MORE THAN ONE QUESTION. THE PLESIOSAUR HAD PREDITORS WHAT WERE THEY? WHAT WAS THERE HABITAT LIKE? What was there eating habits like? What are there characteristics?
from JACKIE, SUNRISE, FL, USA; May 9, 1999
A: Pliosaurs (a type of plesiosaur) preyed upon smaller plesiosaurs. The larger Ichthyosaurs may have eaten young or small plesiosaurs. For information on Plesiosaurs, click here.
Q: My 7-year daughter and I are just beginning to learn about fossils. We have a pick/hammer and safety glasses. I have no idea on how to identify sedimentary rocks or which rocks we should try to crack open. Is there a web-site you could recommend or give us some beginner tips?
from Steve P., Roselle, Illinois, USA; May 8, 1999
A: That's a great idea for an outing! Exposed sedimentary rock is pretty easy to identify - it's in layers. To find an example of exposed sedimentary rock in your area, look at the cut-out area where highways go through hills. The layers should be easily visible. Other places to look are cliffs, rock outcroppings, canyons, badlands, etc. I have a little bit on finding fossils in Zoom Dinosaurs at: /subjects/dinosaurs/dinofossils/Fossilfind.html.
Q: Was there any dinosaur that was found with skin still on it!
from Ryan R., Milton, MA, USA; May 8, 1999
A: Yes, quite a few skin specimens have been found, including bumpy skin (like T. rex) and impressions of proto-feathers or feathers (like Sinosauropteryx). For more information on dinosaur skin, click here.
Q: I am 4 years old, and my question is "IS STEGOSAURUS TAIL HAS POISON IN IT OR NOT" ? Pls answer my question.
from Ashwin K., Boca Raton, FL, USA; May 8, 1999
A: There is no fossil evidence for poison. For more information on Stegosaurus, click here.
Q: Was Pachycephalosaurs an ornithopod?? The Childcraft book Dinosaurs! says yes, but you say no. Is is because the book is 12 years old and this site is only 3??
from Jimmy L., Georgia, USA; May 8, 1999
A: I use the classification system presented in "The Evolution and Extinction of the Dinosaurs" by Fastovsky and Weishampel (1996) . They place Pachycephalosaurs closer to the ceratopsians that ornithopods (based on skull structure), and have the following cladogram:
Ceradpoda:
- Ornithopoda
- Marginocephalia
- Ceratopsia
- Pachycephalosauria
Q: Could you please help me? I need to know what an Xiaosaurus weighed, how it was born, how long it usually lived, and what it looked like. Please help me this is the only place I might be able to get an answer online. Thanks!!!
from Pat K., Pittsburgh, PA, USA; May 8, 1999
A: For information on Xiaosaurus, click here. It probably hatched from eggs, but no Xiaosaurus eggs have been found. I haven't seen a good weight estimate for Xiaosaurus. No one knows how long it lived.
Q: Were triceratops loners ,didn't care for young,or took care of
there babies??
from SIMONE J., WOODBURY, NEW JERSEY, USA; May 7, 1999
A: Triceratops probably lived in herds, but how much (if at all) they cared for their young is unknown. For more information on Triceratops, click here.
Q: What is the height of the dinosaur Eoraptor. Not the length, the height!!! Please answer very soon!
from Elise M., Eliot, Maine, USA; May 6, 1999
A: Eoraptor was a bit under 1 1/2 ft tall. For more information on Eoraptor, click here.
Q: Were all dinosaurs mean?
from Kelsey, USA; May 6, 1999
A: Dinosaurs didn't have complex emotions like meaness (or niceness). They just did what they had to in order to survive. The meat-eaters (like T. rex) ate other animals because they were hungry, not out of malice.
Q: When were the first Stegosaurus bones found?
from ??; May 6, 1999
A: Stegosaurus was first found in 1876 by M. P. Felch. For more information on Stegosaurus, click here.
Q: How long does it take for dinosaur eggs to hatch?
from Bobby F., Mansfield, Texas, USA; May 6, 1999
A: No one knows. For more information on dinosaur reproduction, click here.
Q: What are five different dinosaurs from the Jurrasic period?
from Hangatu H., Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; May 6, 1999
A: For dinosaurs from the early Jurassic period, click here. For dinosaurs from the middle Jurassic period, click here. For dinosaurs from the late Jurassic period, click here.
Q: WHICH ANIMALS LIVED IN THE HOUSTON TEXAS AREA?
from jess, texas, USA; May 6, 1999
A: For some fossils that have been found in Texas (and other states), click here. I don't known which ones were found in the Houston area in particular.
Q: Do the mom dinosaurs look different from the dad dinosaurs? I'd like to know.
from Victoria, Cincinnatti, Ohio, USA; May 5, 1999
A: Nobody knows the answer to this question. Just by looking at the bones of dinosaurs, we can't tell if they're male or female. Some scientists think that male and female of the large-crested dinosaurs (like Parasaurolophus) may have had different sized crests. This is just a guess, but it is based on the fact that for many modern-day animals, horn or antler size (or even their existence) is one way to distinguish between the genders.
For more information on this topic, click here.
Q: when were the first humans on earth.
from DD, Pfafftown, NC, USA; May 5, 1999
A: Scroll down about 5 questions. I just answered this a few days ago.
Q: Hey, I have a question about the Troodon....I was wondering who were its predators?? Did it have any? I am sure it was the big Dinosaurs, right? Please answer me!!! Thanks
from Karly, KC, USA; May 5, 1999
A: It isn't known exactly which animals preyed upon Troodon. This type of information is only known when two animals are found fossilized together in a death grip, or if the bones of one are found inside a fossil of the other. Unfortunately, these finds are rare. Otherwise, all you can do is look at the likely possibilities, and see which predators lived during the same time period and in the same locations. This can lead to incorrect guessing, of course, but is all that is possible before more fossil evidence is found.
Large predators from Troodon's time (and place) include T. rex, Saurornithoides, Nanotyrannus, etc. For other contemporaries of Troodon, click here.
Q: I DONT' HAVE A QUESTION REALLY, MY BIG SISTER WANTS IS DOING A REPORT AND SHE WANTS TO KNOW IF YOU HAVE A PICTURE OF A TROODON...IT WOULD REALLY HELP HER OUT!
from KC, OK, USA; May 5, 1999
A: Yes, click here to see a page about Troodon.
Q: How long can a T-rexes Teeth get? how many pounds of meat does it eat?
from Eric W., Bradford, ILL, USA; May 4, 1999
A: For information on T. rex's teeth, etc., click here.
Q: What is the nickname of Triceratops?
from Sam S., St. Croix Falls, USA; May 4, 1999
A: Most people call Triceratops Triceratops. In the movie "Land Before Time" Triceratops was Sarah. For information on Triceratops, click here.
Q: What does the name Ankylosaurus mean?
from Garrett M., bakersfield, CA, USA; May 4, 1999
A: It means "fused lizard." For more information on Ankylosaurus, click here.
Q: Why do sabertooth tiger have long teeth?
from ERINLEE, Bradford, IL, USA; May 4, 1999
A: Their main food was the thick-skinned large mammals like mastodons. They needed long teeth to pierce the skin and "stab" the prey. For more information on saber toothed cats, click here.
Q: My class is doing bibliographys on dinosaurs and I was wanting to know the definition of; metobolic disease. I know it was a disease that t-rex had, but I need the definition. Please!!!
from Jessica G., Texas City, Texas, USA; May 4, 1999
A: All animals can get metabolic diseases. Metabolic diseases, like gout or diabetes, are diseases in which the body produces a metabolic imbalance (chemical or physical), like too much uric acid in gout, or an inability to metabolize carbohydrates properly in diabetes. These diseases are not contagious, but occur in congenitally predisposed individuals. Some fossilized T. rex bones have shown evidence of gout. For more information on T. rex's gout, click here.
Q: what does ZOOM DINOSAURS mean?
from Shane, Cincinnatti, Ohio, USA; May 4, 1999
A: It means you can zoom in on fact about dinosaurs; you start with the basic information and then zoom in on more advanced details.
Q: Did the t-rex nest and stay with the eggs once they were laid, or did they abandon the eggs right away??
from Joanne L., Scarborough, Ontario, Canada; May 3, 1999
A: No one knows about T. rex's treatment of its eggs. Neither T. rex nests nor eggs have been found. Some of the unidenntifies eggs that have been found may belong to T. rex, but identifying most egg fossils is very difficult (since the embryos inside are usually not preserved).
Q: How long after the dinosaurs became extinct did humans first appear on Earth?
from Cindy D., Pfafftown, North Carolina, USA; May 3, 1999
A: The dinosaurs went extinct about 65 million years ago. People evolved about 200,000 years ago; this is a difference of roughly 65 million years.

Q: Aren't Pteranodons flying dinosaurs?
from Trey G., north little rock, AK, USA; May 3, 1999
A: Pteranodons were flying reptiles, but were not dinosaurs. For more information on Pteranodon, click here.
Q: what is a dinosaur scientist called
from ?; May 2, 1999
A: A paleontologist. For information on some of most famous paleontologists of all time, click here.
Q: How long was the plesiosaur and how much did it weigh?
from Tess S., Center Valley, PA, USA; May 2, 1999
A: Plesiosaurus was about 7.5 feet (2.3 m) long. I've never seen a reliable estimate of its weight. For more information on Plesiosaurus and other Plesiosaurs, click here.
Q: Is there any information about the dinosaur "Saurornithoides" on this website?
from Amitjt A., Carteret, New Jersey, USA; May 2, 1999
A: Yes, look in the Dinosaur Dictionary under S.
Return to the top of the page.
Enchanted Learning®
Over 35,000 Web Pages
Sample Pages for Prospective Subscribers, or click below
Click to read our Privacy Policy
Enchanted Learning Search
|
Search the Enchanted Learning website for:
|
Advertisement.
Advertisement.
Copyright ©1996-2018
EnchantedLearning.com ------ How to cite a web page


 No one knows how a T. rex would clean its teeth or if it even needed to. Since it had replaceable teeth, it probably didn't need to clean its teeth. If one broke off or became worn down, it would be replaced by a new tooth. For more information on T. rex, click here.
No one knows how a T. rex would clean its teeth or if it even needed to. Since it had replaceable teeth, it probably didn't need to clean its teeth. If one broke off or became worn down, it would be replaced by a new tooth. For more information on T. rex, click here.